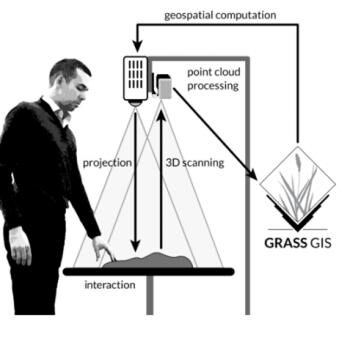
GIS-Based Spatial Analysis using Tangible Landscape: Simulation of Cement Raw Material Exploitation of Karst Area
Indonesia is the biggest country in the South East Asia that have karst landscape. One of the benefit of karst is as the source of cement material. Indonesia is the second larger miners of karst area after Vietnam. One of the most important of karst area is as water resources, therefore karst area is a good for an agricultural activities. South Malang is a one of the karst areas in East Java. The composition of rocks in karst area can be identified from geological map of Badan Geologi, Pusat Survey Geologi (Sheet Turen and Blitar).
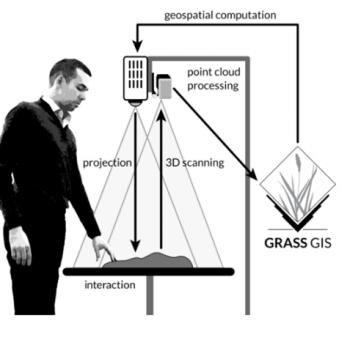
South Malang is a potential area for karst mine and build a cement factory. These activities can cause social conflict caused by the loss of spring and the agriculture, then many potentials of disaster in karst area such as a flood, erosion, water and air pollution, and changing of landscape area will be appears. Actually karst area is the most sensitive and riskiest of building and mining activities, so we need the solution for this problem based-on geospatial technology. Up to present, researches in karst area of South Malang have not completed social and environmental problems, therefore this research is about to simulate and assess the impact of mining in karst area using Tangible -Landscape approach for model the potential negative impacts.